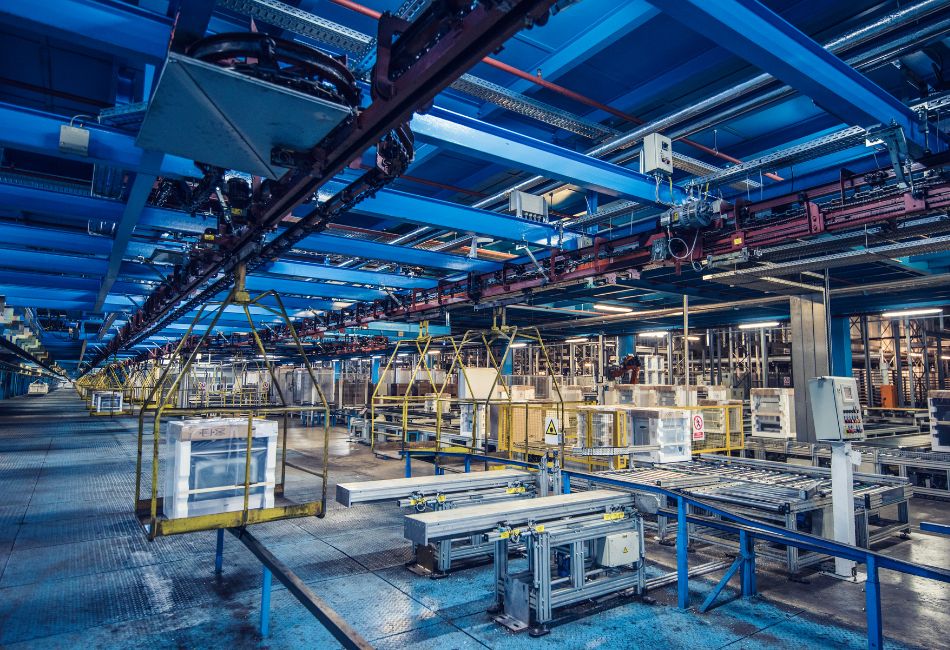
In the manufacturing world, downtime means lost revenue. Every second of disruption can throw productivity schedules off track, potentially leading to lost orders, breaches of contract and substantial losses.
This is why contingency planning is so critical for manufacturing businesses. They tend to have multiple plans in place to cover a wide range of potential scenarios, including using factory backup power solutions to protect against sudden power cuts.
Why Backup Power Is Critical In Manufacturing
Within a manufacturing environment, there are lots of variables you can control from the performance of equipment to the efficiency of processes. However, there are also lots of things you can’t predict, such as extreme weather, natural disasters and localised faults with the power grid.
You can’t stop these unexpected events from happening, but you can put a few safety nets in place to mitigate the impact.
This is where backup power comes in. Most factories will have emergency generators for production lines and other critical systems, which are ready to kick in the second a mains power outage is detected. This can provide vital temporary power to keep things running until the fault can be fixed or the power comes back online.
Without it, the whole operation could shut down. Manufacturing facilities need to keep production lines running 24/7 in many cases, in order to meet extremely tight order deadlines. In these high-pressure operations, even just a few minutes of downtime is unacceptable.
It can mean angry customers and lost orders, and throw production schedules into disarray. Machinery and equipment could be damaged by the sudden halt to production. It could even cause safety issues, where workers are using dangerous machinery and the lights suddenly go out.
Ultimately though, it means lost revenue. A shocking statistic from global IT consultancy IDS-INDATA predicts that UK and European manufacturers will lose over £80 billion due to downtime in 2025.
Diesel Generators Keeping Production Lines Running
Diesel generators are the go-to source of backup power for manufacturing industries across the world. There’s a very good reason for this, as they are dependable, respond quickly, are capable of handling high loads (when properly sized) and are widely available.
When installed, they can provide support to power a full range of mission-critical systems within factories. This includes:
- Heavy machinery and equipment
- Conveyor systems
- Robotics and AI-powered technology
- Climate control systems
- Safety systems
Generators can also be scaled to suit demand, providing backup power for single production lines or entire facilities.
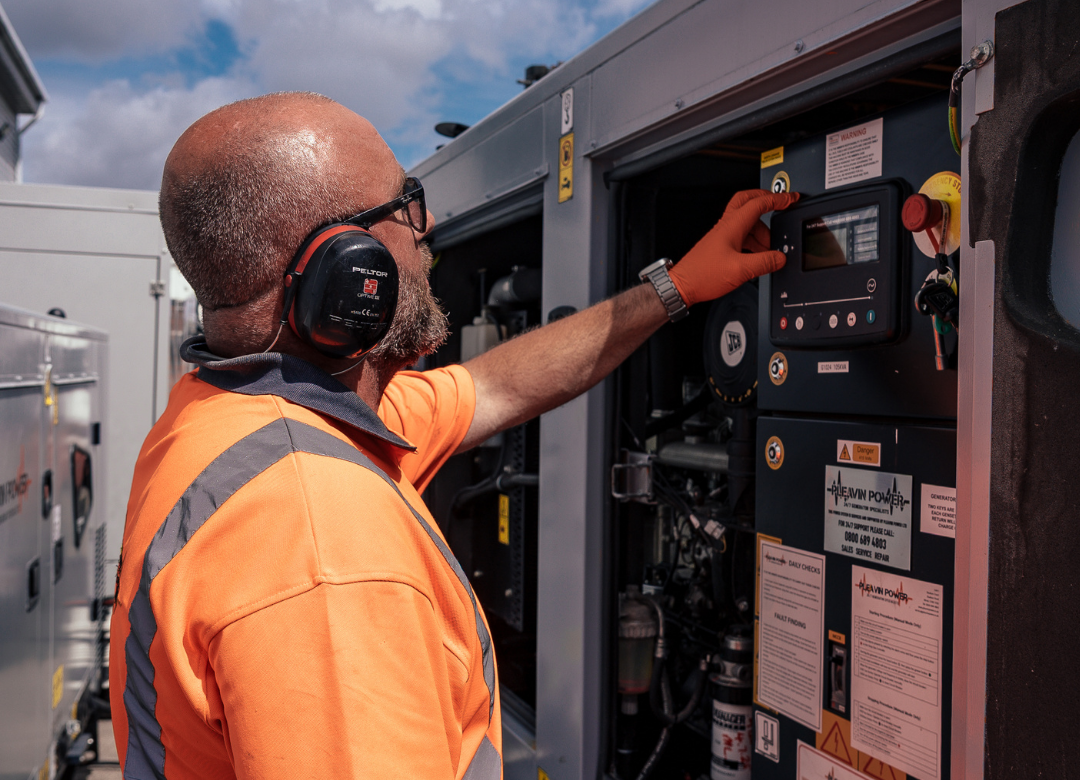

Load Bank Testing For Reliable Operation
To work effectively, emergency generators need to be regularly maintained and tested. One of the most crucial types of proactive maintenance is load bank testing.
Carried out by an expert in manufacturing generator solutions, this involves using equipment to simulate a full electrical load in ‘real world’ conditions. The aim is to check how the generator will perform in a real situation, such as a power outage.
Load bank testing has a number of other benefits, including:
- Detecting hidden faults
- Ensuring fuel and cooling systems are ready for use
- Flagging up issues with generator size or capacity, in case new equipment needs to be bought or hired
Planning For Manufacturing Power Outages
Planning ahead can save manufacturing facility operators all kinds of headaches further down the line. The main goal is to reduce disruption, but comprehensive power continuity planning can also help the facility and the business to become more resilient in general. You’ll know that whatever happens, whether it is inside or outside of your control, the factory will keep on running.
The main steps in a manufacturing continuity power plan include:
- Risk assessment – identifying vulnerable processes, worst case scenarios and assessing the likely impacts of a power outage or other significant disruption
- Sizing power needs – bringing in a specialist to carry out an on-site assessment, and match generator capacity to production demand.
- Installation and integration – planning a schedule for works to minimise disruption and ensure a seamless switchover
- Regular testing and drills – including preparing staff for real scenarios

Hire vs Buy Generator Solutions
One of the choices you’ll make when implementing your power backup plan is whether to hire or buy a generator.
Industrial generator hire has its advantages, including a lower upfront cost. There’s also a degree of flexibility, where a generator can be used to cover seasonal spikes in production demand or other short-term projects. Your facility may not be quite ready for the long-term commitment and upfront costs of a permanent generator installation/
However, in most cases, buying a generator is almost always the most cost-effective solution in the long run. It ensures permanent protection, no matter what may happen.
To make your decision, it’s important to factor in the size of the facility and the permanence of your site (how long you expect to stay there). You’ll also need to think about your budget, power demands and the frequency of power outages you’ve experienced over the last few years.
You may want to start with a hybrid approach, buying a generator to cover core needs and hiring extra equipment during busy peak seasons.
Maintenance Strategies To Avoid Downtime
Once you’ve decided on a strategy and developed a continuity power plan for your facility, the next step is to put a maintenance schedule in place. Don’t delay in starting this: Think of it as crucial preventative maintenance.
Regular checks should include:
- Fuel checks, coolant inspections and oil changes
- Control system updates
- Regular servicing
- Load bank testing
- Predictive maintenance, such as remote data monitoring
To develop a suitable maintenance schedule for your generator, it’s best to get advice from an expert.